Table of Contents
- Part 1: What is THC?
- Part 2: What is CBD?
- Part 3: Comparing THC vs CBD
Lately, it seems like CBD, Cannabidiol, and Cannabinoids are buzz words for every beauty product, health food, or anti-anxiety promotion on the market.
So-called “CBD-infusions” are being touted in everything from youth serums to smoothies, and Carl’s Junior even shockingly debuted a CBD-infused burger on this year’s 4/20 celebration.
Celebrities like Kim Kardashian are jumping on the CBD bandwagon with events like her “CBD and mediation-themed baby shower”, where A-list celebs “zenned out” with CBD products and sound baths. Jennifer Aniston and Mandy Moore swear by CBD oil to keep their stress, anxiety, and pain under control.
But what is CBD really, and does it actual work?
Is it cannabis, is it hemp, and what is the difference between THC and CBD?
Let’s cut through the hype, and find out about the real differences and similarities between the two compounds, their benefits, effects and uses, and what both CBD and THC can do to enhance your life.
What is THC?
Let’s first start with the basics of THC, where it comes from, and what kind of effects it has on the body.
What does THC stand for?
THC means Tetrahydrocannabinol and it is one of the two primary cannabinoids that occur naturally in the Cannabis plant.
What does THC do?
While both THC and CBD interact with the cannabinoid receptors found in the human body and brain, their psychological and physical effects can differ dramatically.
THC is the main psychoactive component of our favorite plant, meaning that THC is the primary component that creates the ‘high’ associated with recreational cannabis use.
THC is a chemical secreted by the glands of the marijuana plant, and occurs mostly in the reproductive organs, and in the female plant, in the resin glands of the bud and flowers.
THC Side Effects
This compound works by mimicking the effects of 2-AG and anandamide, which are neurotransmitters produced naturally by the human body. These help to modulate sleeping and eating habits, the perception of pain, and countless other bodily functions, which is why THC can have many medical properties as well as recreational uses.
Although THC is only one of 85 plus chemical compounds known as cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, THC is the primary psychoactive ingredient. It mainly occurs in the cannabis plant as a natural defense against viruses, parasites, and bacteria with antibacterial qualities.
It’s pretty common knowledge that THC is what creates the “cerebral” effect we associated with getting stoned, but what’s actually happening inside your body when you light up a joint or pop an edible?
When you decombust THC via a bowl, joint, or dab, it immediately gets released into your blood and swims quickly upstream, reaching your brain in just a matter of seconds.
THC then mimics cannabinoid chemicals that occur naturally in the body and attaches itself to your cannabinoid receptors. Here’s a diagram that outlines how THC interacts with the different part of your brain.
Taking edibles, on the other hand, may take as little as 30 minutes or as long as 4 hours to have the same effect, which is why edibles companies always suggest you “start low and go slow”… there isn’t any going back from feeling “too high” until the cannabinoids have worked their way out of your system over several hours.
Cannabinoid receptors are located in your cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. They cause functions like thinking, memory, motor movements, pleasure, coordination, and concentration, and are typically slowed when they come into contact with THC, which causes the (usually) pleasant physiological responses of feeling sleepy, calm, and relaxed.
The reason THC affects these areas so much more than other active cannabinoids, like CBD, comes down to its actual shape. Because of its molecular structure, THC binds securely to your neurotransmitters – the spaces that carry communication between your neurons.
This graphic is here to give you a visual representation of how THC and the endocannabinoid system works in the body.
It mimics anandamide (otherwise known as the bliss molecule), which is a natural cannabinoid found in the body. That’s why you’ll often find yourself easily laughing, enjoying yourself (and food) and are just easily overly-stimulated while you’re stoned… you’ve literally blissed yourself out! Sometimes these blissed-out feelings are so good that they overtake your brain’s short-term memory, another commonly-known side effect of regular cannabis consumption.
THC temporarily inhibits your hippocampus, which is the brain’s control center for all of your memories. On top of short-term and temporary memory loss, other side effects of too much THC may also include dizziness, anxiety (we’ve all been there!), or fatigue. Physical effects can include pain inhibition, a slowing down of motor movements, dry mouth and an increase in appetite.
Please keep in mind that every body is affected a little (or a lot) differently by THC, and that even without regular use, people have a wide variety of tolerances for both psychological and physical effects of smoking, dabbing, tinctures, and edibles, sometimes varying widely between different methods of consumption.
Popular High THC Strains
For consumers with an impressive tolerance or looking for heavy pain relief, there are options for strains known for being high in THC content. Favorites like Bruce Banner, Girl Scout Cookies, Ghost OG, Chemdawg, and The White regularly come in at over 20% THC content.
What is CBD?
It is one of most critical cannabinoids contained in the cannabis plant, and is the second naturally occurring primary cannabinoid behind THC.
What does CBD Stand for?
CBD stands for Cannabidiol. It exists both in hemp and cannabis, and while cannabinoids are present within several plants in nature, cannabis is the only plant known to contain actual CBD.
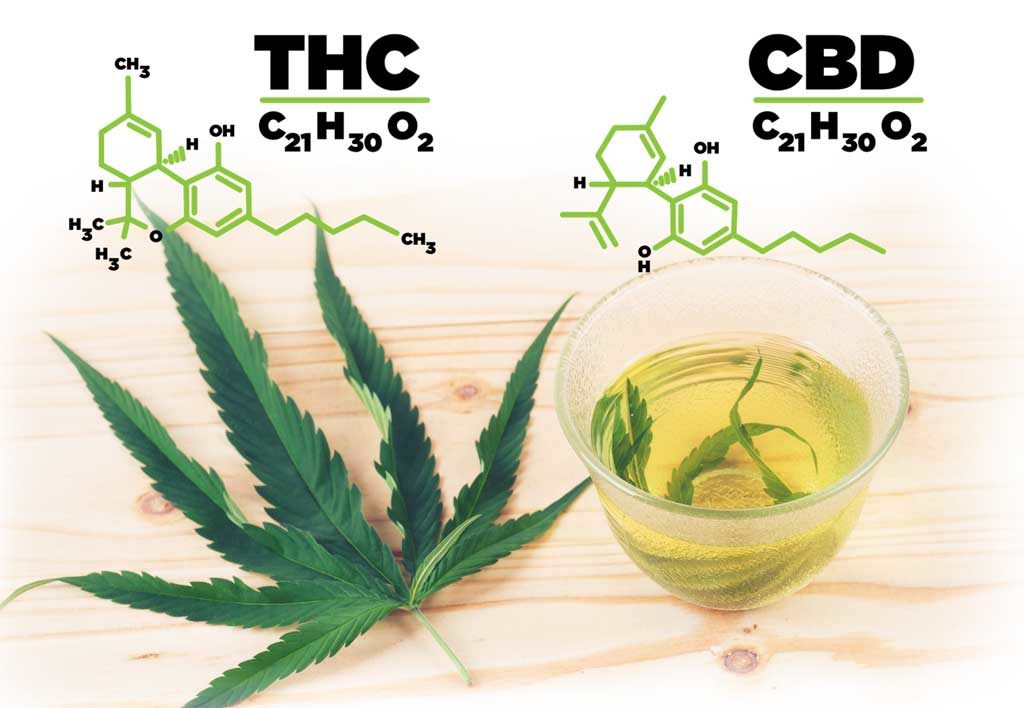
CBD vs THC Molecule and Chemical Composition
CBD and THC have the exact same chemical makeup: 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. They are very nearly identical twins, except for the varied arrangement of this single atom.
While CBD has the same chemical formula as THC, the shape of the molecules and the structure of the atoms are in a different arrangement. This very slight variance causes THC to create a psychoactive effect we all know and love, while CBD does not give us this same “buzz”.
What does CBD do and how does it work?
While there are still slight psycho-active effects, this fact means that when you ingest CBD for medical purposes, you will more likely experience an absence of your unwanted discomfort, with little or no noticeable effect on your cognitive abilities.
CBD Side Effects
Will CBD get you high?
High-CBD strains tend towards clear-headed and very functional effects without the euphoric high associated with high-THC strains. They’re typically preferred by consumers who are extremely sensitive to the side effects of THC, and want to experience relief instead of a “high”.
A CBD-dominant strain is often used by patients who need to medicate throughout the day to control anxiety, inflammation, chronic pain, or other chronic conditions.
It’s easy to get overwhelmed by the wide variety of CBD-infused products, a CBD burger isn’t going to give you the same sort of relief a concentrated oil would give for medical conditions and relief.
While CBD will not produce most of the psychoactive effects you might experience with THC, if you take too much, you may still get a bit of drowsiness, dry mouth, or lightheadedness. Feeling lightheaded is caused by a small drop in blood pressure, which is not dangerous but can be uncomfortable. These side effects can be easily remedied by consuming a lightly caffeinated beverage and staying hydrated.
How to Take CBD
First, consider what part of your body is in need of treatment, because in order for this helpful molecule to be effective, it must get to where it’s needed. If your pain is located on your skin or a mucus membrane, you could first try a localized product like a topical or suppository, which delivers the highest concentration of CBD exactly where you want it.
Otherwise, CBD needs to travel through your digestive system and bloodstream to reach where it’s headed, which is when it’s best to use a vaporizer or oral product like an oil or a tincture for quickest relief.
Options for ingestion include Oral (swallowed, like edibles, tinctures, oil, or capsules), Oral (sublingual, like oils or tinctures), Inhalation (vape pens or dabs), Topicals (creams and lotions), and Vaginal and Anal (suppositories and creams).
What is CBD Oil?
CBD oil derived from the Cannabis plant is what is known scientifically as cannabidiol. Hemp oil, is extracted from the leaves, petals and seeds from a hemp plant. Cannabis sativa plants have varying levels of THC depending on strain, which one of the differences in defining hemp oil versus CBD oil.
A cannabis sativa plant that contains more than 0.3% of THC is considered to be what we know as marijuana, but the same plant containing less than 0.3% THC is considered hemp. Therefore, even though Cannabis sativa and hemp are derived from the very same species of plant, they are different based on the plant’s THC levels.
This can be a bit confusing, as CBD oil and hemp oil do have a lot in common: neither is linked to THC and therefore won’t provide that feeling of being “stoned” so often attributed to THC. Structurally, the primary variance between hemp oil and CBD oil is that hemp oil can only be extracted from a hemp plant. On the other hand, CBD oil can be extracted from a variety of plants, including hemp plants, marijuana plants, and a variety select other plants as well.
Popular High CBD Strains
Because of the growing popularity happening around CBD, more growers have focused on cross-breeding breeding indica, sativa and hybrid strains that have low THC levels and high CBD content.
Some of the more prominet CBD strains are Charlotte’s Web, Harlquien, ACDC, Harle-Tsu, Canna-Tsu, Ringo’s Gift and Pennywise just to name a few.
Comparing THC vs CBD
We’ve already covered the different structures of CBD and THC and their varying effects, so it depends on the desired outcome of your cannabinoid usage whether you’ll want to use a product with a higher THC or CBD content.
While CBD and THC both bind tightly to the CB2 receptor as discussed earlier, they interact with the CB1 receptor in different ways. THC is able to bind directly with CB1 receptors, which creates a reaction that sends psychoactive signals to the brain… this is when you start to feel “high.” In contrast, CBD does not bond directly with the CB1 receptor, and can even remove the bond between THC and the CB1 receptors… this is why CBD is often an effective treatment of a person who is feeling anxious, dizzy, or “too high” from smoking or eating too much THC!
THC vs CBD Benefits
Both THC and CBD offer a huge variety of health benefits, and together are often the most effective for medical treatments. Although THC’s mind-altering effects aren’t preferred by everyone, many medical professionals in the cannabis industry do prescribe to the “whole plant theory” of using both CBD and THC for maximum health benefits, and treatments of chronic health conditions, cancer, fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, seizures, and epilepsy. CBD, and CBD oil in particular, can still deliver many of the same benefits of THC without inducing most of its psychoactive effects, and is commonly used in treatment of anxiety, pain, and many inflammatory diseases and conditions.
Conclusion
While cannabis remains illegal, especially recreationally, in much of the world and the United States, the Farm Bill, which passed in 2018, legalized CBD nationwide in the US. Therefore, CBD is often more readily available and easily accessible for patients needing treatment, although the source of the CBD should always be verified for maximum value.
Basically, know what you’re buying, know how much you’re taking, and make sure you know the best way to fix what ails you… there are lots of different options available in both THC and CBD products, from creams to flower to pills to oils. Cannabis terpenes can even be found in essential oils, candles, and aromatic options.
Cannabis is a miracle plant, and with recent legalization in many states, we are only at the brink of beginning to discover how spectacular it can be for health, our lives, and our society.